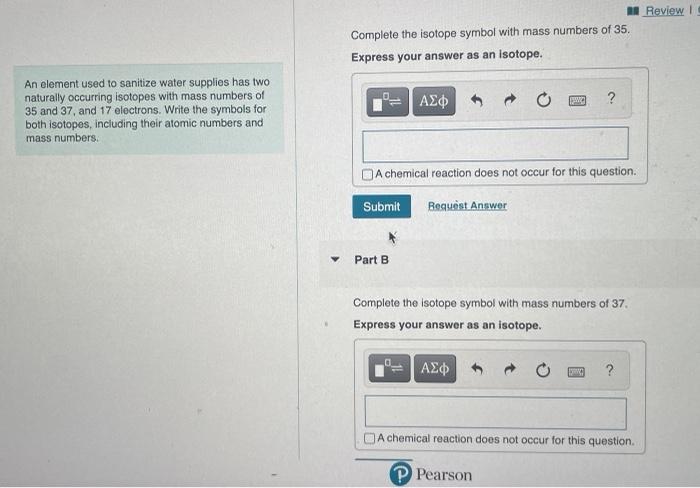
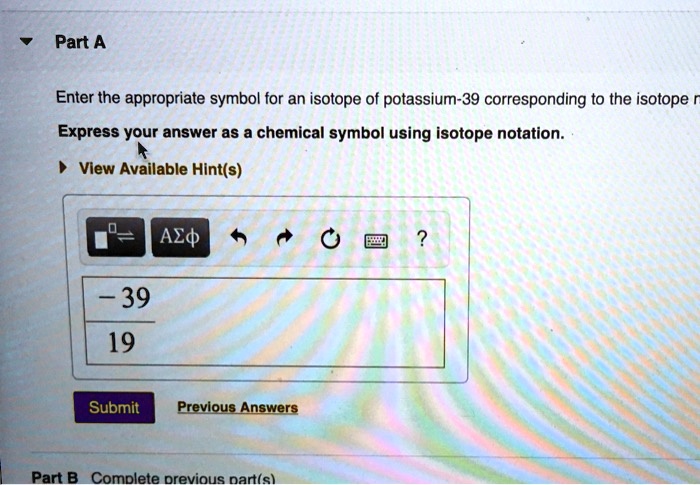
Express your answer as an isotope – a concept that encapsulates the very essence of matter. Isotopes, atoms with varying neutron counts, offer a fascinating lens through which we can explore the intricacies of the physical world. Their unique properties and diverse applications make them indispensable tools in fields ranging from medicine to environmental science.
Embark on an enlightening journey as we delve into the captivating realm of isotopes, uncovering their significance and unlocking their potential.
Isotopes, the building blocks of matter, possess distinct characteristics that set them apart. Their varying masses, atomic numbers, and stability influence their behavior and applications. In medicine, isotopes like iodine-131 play a crucial role in diagnosing and treating thyroid disorders.
Geologists utilize isotopes to unravel Earth’s history and determine the age of rocks. Environmental scientists leverage isotopes to track pollutants and monitor ecosystem health. The versatility of isotopes extends far and wide, offering invaluable insights into the workings of our world.
1. Isotope Definitions: Express Your Answer As An Isotope
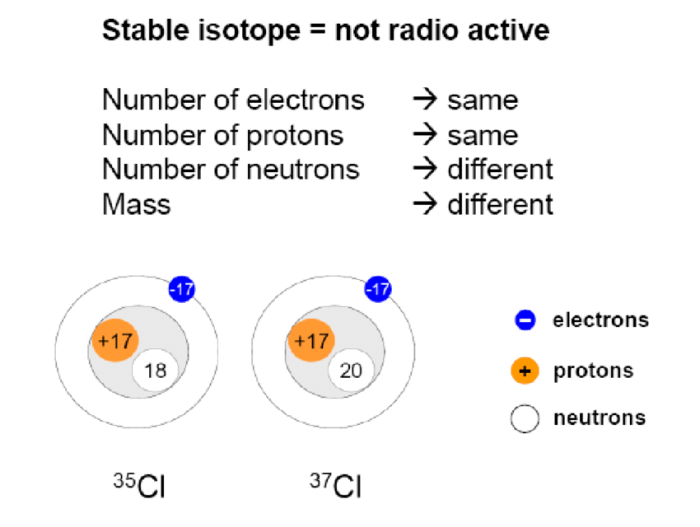
Isotopes are variants of an element that have the same atomic number but different numbers of neutrons. This difference in neutron count results in different masses for each isotope. Isotopes are significant because they provide valuable insights into the structure and behavior of elements and play crucial roles in various scientific disciplines.
Examples of different isotopes include:
- Hydrogen: 1H (protium), 2H (deuterium), 3H (tritium)
- Carbon: 12C, 13C, 14C
- Uranium: 235U, 238U
2. Isotope Properties
Isotopes exhibit unique properties that distinguish them from each other. These properties include:
- Mass:Isotopes of the same element have different masses due to the varying number of neutrons. This difference in mass affects their physical and chemical properties.
- Atomic Number:All isotopes of an element have the same atomic number, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus. This determines the element’s chemical identity.
- Stability:Isotopes can be stable or radioactive. Stable isotopes have a balanced neutron-to-proton ratio, while radioactive isotopes have an unstable ratio and undergo decay.
3. Isotope Applications
Isotopes have a wide range of applications in various fields:
- Medicine:Radioactive isotopes are used in medical imaging, cancer treatment, and radiation therapy.
- Geology:Isotopes are used to determine the age of rocks and fossils, study geological processes, and explore mineral deposits.
- Environmental Science:Isotopes are used to trace pollutants, monitor water quality, and study climate change.
The advantages of using isotopes include their specificity, sensitivity, and ability to provide unique insights into complex systems. However, limitations include the potential for radiation hazards and the need for specialized equipment and expertise.
FAQ Corner
What is an isotope?
An isotope is an atom of a particular element with a specific number of protons and electrons, but a varying number of neutrons.
How are isotopes used in medicine?
Isotopes are used in medicine for diagnostic imaging, radiation therapy, and targeted drug delivery.
What is the difference between a stable and a radioactive isotope?
Stable isotopes do not undergo radioactive decay, while radioactive isotopes decay over time, emitting radiation.