Exercise 3 review sheet the microscope – Exercise 3 Review Sheet: The Microscope delves into the fascinating world of microscopy, unveiling its significance in scientific research and exploring the diverse applications of various microscope types. This guide provides a thorough overview of the structure and function of a compound light microscope, equipping readers with the knowledge and skills to effectively utilize this essential scientific tool.
Through hands-on exercises and comprehensive explanations, this review sheet empowers students to master the proper setup, use, and maintenance of a microscope. It delves into the preparation of microscope slides, the art of observing specimens, and the utilization of stains to enhance visualization.
Furthermore, it offers practical tips for capturing clear and informative photomicrographs, enabling students to document their observations with precision.
Introduction: Exercise 3 Review Sheet The Microscope
Microscopy is a powerful tool that has revolutionized the field of scientific research. Microscopes allow scientists to observe and study objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. This has led to a greater understanding of the structure and function of cells, tissues, and organs, as well as the microorganisms that inhabit them.
There are many different types of microscopes, each with its own unique advantages and applications. The most common type of microscope is the compound light microscope, which uses visible light to illuminate the specimen. Other types of microscopes include electron microscopes, which use a beam of electrons to create a magnified image, and scanning probe microscopes, which use a sharp probe to scan the surface of a specimen.
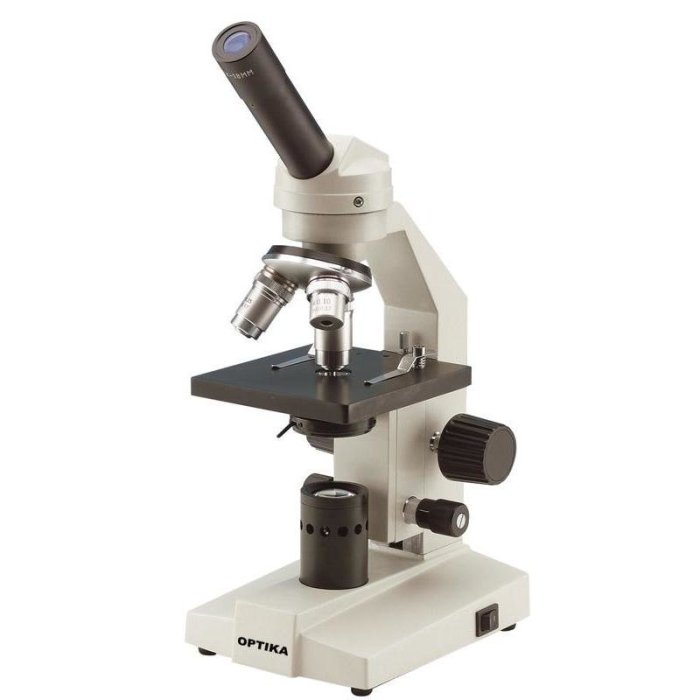
Using a Microscope, Exercise 3 review sheet the microscope
Using a microscope properly is essential for obtaining clear and informative images. The first step is to set up the microscope correctly. This involves placing the microscope on a stable surface and adjusting the height of the stage so that the specimen is in focus.
The next step is to focus the microscope. This is done by adjusting the coarse and fine focus knobs until the specimen is sharp and clear.
Once the microscope is focused, the illumination can be adjusted. The intensity of the light can be increased or decreased using the diaphragm. The condenser can be moved up or down to change the angle of the light. The field diaphragm can be used to control the amount of light that enters the microscope.
Observing Specimens
When observing specimens under a microscope, it is important to use the correct magnification. The magnification of a microscope is determined by the objective lens and the eyepiece. The objective lens is the lens that is closest to the specimen, and the eyepiece is the lens that the viewer looks through.
The magnification of a microscope is calculated by multiplying the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece.
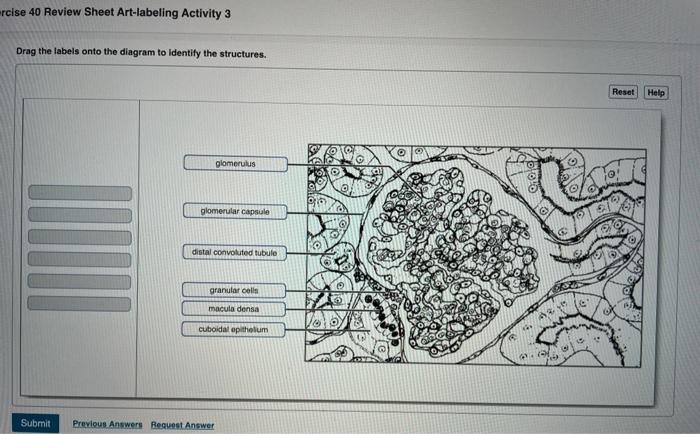
There are many different types of microscope slides, each with its own unique purpose. The most common type of microscope slide is the glass slide. Glass slides are used to hold specimens that are transparent or semi-transparent. Other types of microscope slides include plastic slides, metal slides, and ceramic slides.
Review Sheet
Questions:
- What are the different types of microscopes and their applications?
- How do you properly set up and use a compound light microscope?
- What are the different types of microscope slides and how are they used?
- How do you observe specimens under a microscope?
Answer Key:
-
- Compound light microscope: Used to observe specimens that are transparent or semi-transparent.
- Electron microscope: Used to observe specimens that are very small or thin.
- Scanning probe microscope: Used to observe the surface of specimens.
-
- Place the microscope on a stable surface.
- Adjust the height of the stage so that the specimen is in focus.
- Focus the microscope using the coarse and fine focus knobs.
- Adjust the illumination using the diaphragm, condenser, and field diaphragm.
-
- Glass slides: Used to hold specimens that are transparent or semi-transparent.
- Plastic slides: Used to hold specimens that are not transparent.
- Metal slides: Used to hold specimens that are magnetic.
- Ceramic slides: Used to hold specimens that are heat-resistant.
-
- Use the correct magnification.
- Prepare the specimen correctly.
- Use the proper illumination.
FAQ Summary
What is the primary function of a microscope?
A microscope’s primary function is to magnify objects, enabling the observation of fine details and structures that are invisible to the naked eye.
What are the different types of microscopes?
There are various types of microscopes, each with its unique capabilities. Some common types include compound light microscopes, electron microscopes, and scanning probe microscopes.
How do I prepare a microscope slide?
Microscope slide preparation involves placing a thin specimen onto a glass slide and covering it with a coverslip to create a stable and clear viewing environment.
What is the purpose of staining in microscopy?
Staining is a technique used to enhance the visibility of specific structures or components within a specimen by adding dyes or stains that bind to specific molecules.
How do I capture a clear photomicrograph?
To capture a clear photomicrograph, ensure proper focus, adjust the illumination, and use a camera with appropriate resolution and settings.