Experiment 8 Limiting Reactant Report Sheet: A Comprehensive Guide embarks on an intellectual journey that unravels the intricacies of chemical reactions and their limiting reactants. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the topic, encompassing theoretical foundations, practical applications, and detailed instructions for conducting and analyzing experiments.
Delving into the heart of the matter, this guide meticulously defines limiting reactants, elucidates their significance, and equips readers with a robust understanding of their identification. It meticulously dissects the structure of Experiment 8 Limiting Reactant Report Sheet, providing a clear understanding of its components and their respective functions.
Limiting Reactant Identification: Experiment 8 Limiting Reactant Report Sheet
In a chemical reaction, a limiting reactant is the reactant that is completely consumed, thereby limiting the amount of product that can be formed. It plays a crucial role in determining the stoichiometry and efficiency of the reaction.
Definition of Limiting Reactant
A limiting reactant is the reactant present in the smallest mole ratio relative to the stoichiometric ratio required for the reaction to proceed completely. In other words, it is the reactant that runs out first, preventing the complete consumption of other reactants.
Identifying the Limiting Reactant
- Compare the mole ratios of each reactant to the stoichiometric ratio.
- The reactant with the smallest mole ratio is the limiting reactant.
- Calculate the theoretical yield of the product using the mole ratio of the limiting reactant.
Experiment 8 Limiting Reactant Report Sheet Structure
Purpose of the Report Sheet
The Experiment 8 Limiting Reactant Report Sheet provides a structured format for recording data, performing calculations, and reporting the results of an experiment designed to determine the limiting reactant in a chemical reaction.
Typical Sections
- Introduction:Background information and purpose of the experiment.
- Procedure:Step-by-step instructions for conducting the experiment.
- Data Collection:Table or chart for recording experimental data.
- Calculations:Equations and steps for determining the limiting reactant and theoretical yield.
- Results:Identification of the limiting reactant and calculated theoretical yield.
- Discussion:Analysis of the results and potential sources of error.
Sample Report Sheet
| Section | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction | Background and purpose of the experiment |
| Procedure | Step-by-step instructions |
| Data Collection | Table for recording experimental data |
| Calculations | Equations and steps for determining the limiting reactant and theoretical yield |
| Results | Identification of the limiting reactant and calculated theoretical yield |
| Discussion | Analysis of the results and potential sources of error |
Data Collection and Analysis

Methods for Data Collection
- Mass Measurement:Use a balance to measure the mass of reactants and products.
- Volume Measurement:Use graduated cylinders or pipettes to measure the volume of liquids.
- Spectrophotometry:Measure the absorbance of solutions to determine the concentration of reactants or products.
Importance of Accurate Data Collection
Accurate data collection is crucial for reliable results. Errors in data can lead to incorrect identification of the limiting reactant and inaccurate calculation of the theoretical yield.
Data Analysis
- Convert experimental data into moles using molar mass or concentration.
- Compare the mole ratios of reactants to the stoichiometric ratio.
- Identify the reactant with the smallest mole ratio as the limiting reactant.
Calculations and Reporting
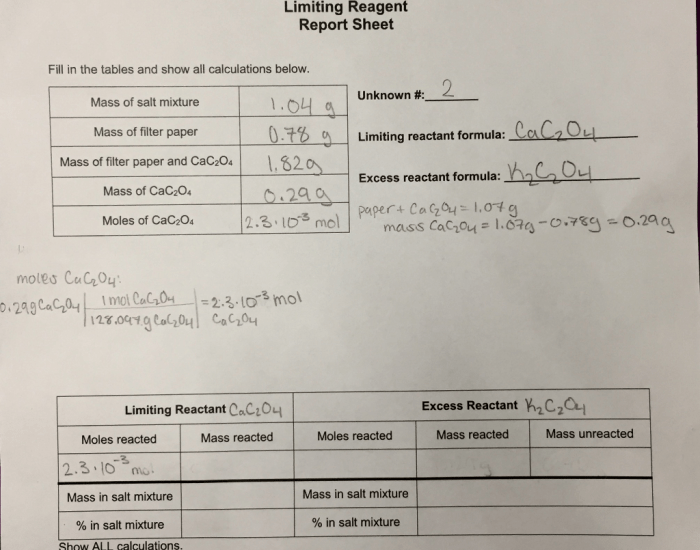
Calculations for Limiting Reactant
- Convert reactant masses or volumes to moles.
- Divide the moles of each reactant by its stoichiometric coefficient.
- The reactant with the smallest mole ratio is the limiting reactant.
Theoretical Yield Calculation
- Use the stoichiometric ratio to determine the moles of product that can be formed from the limiting reactant.
- Convert the moles of product to mass or volume using molar mass or density.
Reporting Results
- Clearly state the identified limiting reactant.
- Report the calculated theoretical yield.
- Discuss any assumptions or limitations of the experiment.
Error Analysis and Discussion
Potential Sources of Error
- Measurement errors (mass, volume, concentration)
- Incomplete reactions
- Contamination
- Incorrect stoichiometry
Minimizing Errors
- Use calibrated equipment.
- Repeat measurements to improve accuracy.
- Control reaction conditions to minimize side reactions.
- Verify stoichiometry through research or experimental data.
Reflection and Discussion
Encourage students to reflect on the experiment and discuss their findings. This could include:
- Evaluation of the accuracy of their results.
- Identification of potential sources of error.
- Suggestions for improving the experiment.
Additional Considerations
Factors Affecting Limiting Reactant, Experiment 8 limiting reactant report sheet
- Stoichiometry:The mole ratio of reactants determines the limiting reactant.
- Reaction Conditions:Temperature, pressure, and catalysts can affect reaction rates and the identity of the limiting reactant.
- Purity of Reactants:Impurities can affect the stoichiometry and thus the limiting reactant.
Importance of Stoichiometry and Reaction Conditions
Understanding stoichiometry and controlling reaction conditions is essential for predicting and controlling the outcome of chemical reactions. It allows chemists to optimize reactions for efficiency and minimize waste.
Real-World Applications
- Industrial Chemistry:Determining the limiting reactant is crucial for optimizing production processes and reducing costs.
- Environmental Science:Understanding limiting reactants helps predict the impact of pollutants on ecosystems.
- Medicine:Identifying the limiting reactant in metabolic pathways is essential for developing effective treatments.
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of identifying the limiting reactant?
Identifying the limiting reactant is crucial because it determines the maximum amount of product that can be formed in a chemical reaction. It allows chemists to optimize reaction conditions and predict the yield of the desired product.
How can errors in data collection affect the accuracy of the limiting reactant determination?
Errors in data collection can lead to incorrect identification of the limiting reactant. Inaccurate measurements of reactants or products can skew the calculations and result in misleading conclusions.
What are some practical applications of limiting reactants in real-world scenarios?
Limiting reactants play a vital role in various industrial processes, such as manufacturing fertilizers, pharmaceuticals, and fuels. Understanding limiting reactants enables industries to optimize production efficiency and minimize waste.