How many chiral carbons are contained in the following structure? This question lies at the heart of organic chemistry, where understanding the chirality of carbon atoms is crucial. Chiral carbons, with their unique spatial arrangements, play a pivotal role in determining the properties and behavior of molecules.
In this exploration, we delve into the concept of chiral carbons, unraveling the criteria for their identification and developing a systematic approach to counting them within molecular structures. Along the way, we uncover the significance of chiral carbons in various scientific disciplines, highlighting their impact on biological activity and molecular properties.
How Many Chiral Carbons Are Contained in the Following Structure?
1. Definition of Chiral Carbons
Chiral carbons, also known as stereogenic centers, are carbon atoms that are bonded to four different substituents. They are significant in organic chemistry because they give rise to stereoisomers, which are molecules that have the same molecular formula but differ in the spatial arrangement of their atoms.
Criteria for Determining Chirality in Carbon Atoms, How many chiral carbons are contained in the following structure
A carbon atom is considered chiral if it meets the following criteria:
- It is bonded to four different substituents.
- It has a tetrahedral geometry.
2. Identifying Chiral Carbons in a Structure: How Many Chiral Carbons Are Contained In The Following Structure
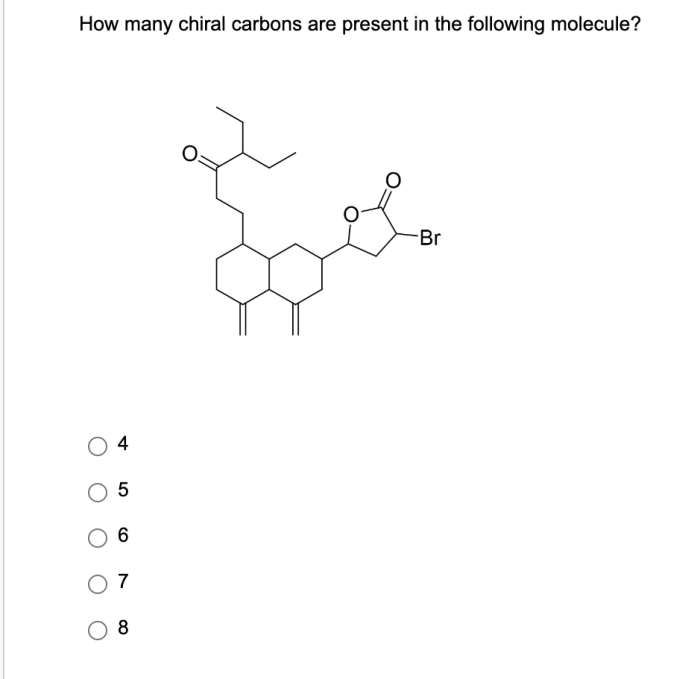
To identify chiral carbons in a molecular structure, follow these steps:
- Examine each carbon atom in the structure.
- Determine if the carbon atom is bonded to four different substituents.
- If the carbon atom meets this criterion, check if it has a tetrahedral geometry.
- If both criteria are met, then the carbon atom is chiral.
3. Counting Chiral Carbons
To count the number of chiral carbons in a molecule, follow these steps:
- Identify all the chiral carbons in the molecule using the method described in Section 2.
- Count the number of chiral carbons.
- The number of chiral carbons is equal to the number of stereoisomers that the molecule can have.
4. Examples of Chiral Molecules
| Molecule | Number of Chiral Carbons |
|---|---|
| 2-Butanol | 1 |
| 3-Methyl-2-butanol | 2 |
| 2,3-Dimethyl-2-butanol | 3 |
5. Significance of Chiral Carbons
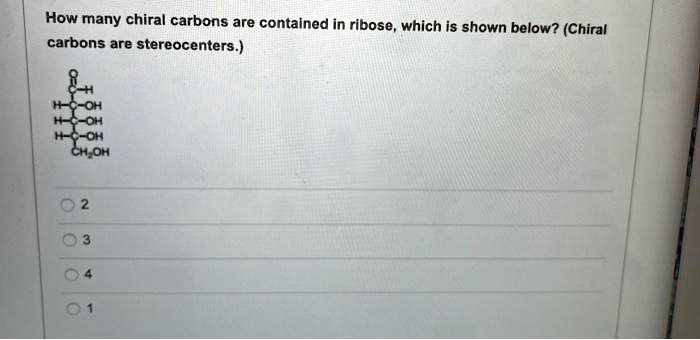
Chiral carbons are important in various fields, including:
- Pharmaceuticals: Chiral drugs interact with biological molecules in different ways depending on their chirality, which can affect their efficacy and safety.
- Biochemistry: Many biological molecules, such as proteins and carbohydrates, are chiral and their chirality plays a crucial role in their function.
- Materials science: Chiral materials have unique optical and electronic properties that can be exploited for various applications, such as in the development of chiral liquid crystals and sensors.
Expert Answers
What is the significance of chiral carbons?
Chiral carbons are crucial in determining the biological activity and molecular properties of organic compounds. They play a vital role in drug development, as different enantiomers of a chiral drug can have vastly different effects on the body.
How can I identify chiral carbons in a molecular structure?
To identify chiral carbons, examine the molecular structure and look for carbon atoms that are bonded to four different groups. These carbons are considered chiral centers.
What is the difference between a chiral molecule and an achiral molecule?
A chiral molecule is a molecule that is not superimposable on its mirror image, while an achiral molecule is superimposable on its mirror image. The presence of chiral carbons contributes to the chirality of a molecule.