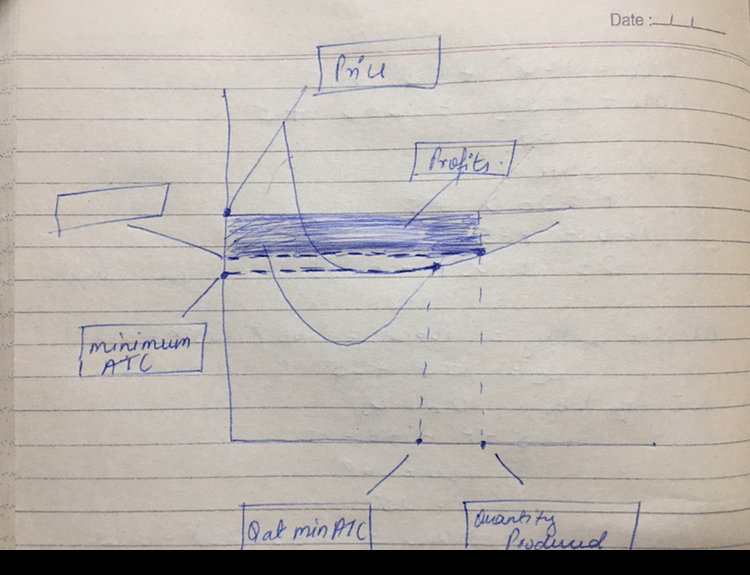
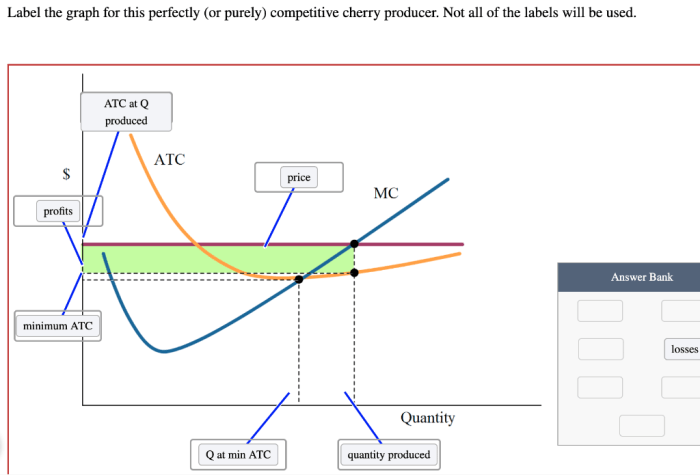
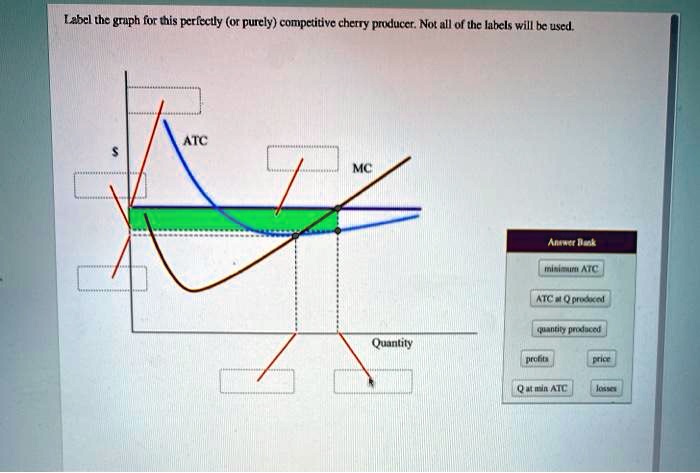
Label the graph for this perfectly competitive cherry producer – In this exploration, we delve into the fascinating world of perfect competition, examining the intricacies of a perfectly competitive cherry producer. By labeling the graph for this producer, we gain insights into the interplay between supply and demand, the determination of equilibrium price and quantity, and the producer’s profit-maximizing output.
As we navigate this topic, we will uncover the fundamental principles governing perfectly competitive markets, shedding light on the role of government policies in shaping market outcomes.
Market Structure
Perfect competition is a market structure in which there are many buyers and sellers, and each firm produces an identical product. In a perfectly competitive market, no single firm has the power to influence the market price.A perfectly competitive cherry producer operates by taking the market price as given and producing the quantity of cherries that maximizes its profit.
The producer’s profit is the difference between the total revenue it receives from selling cherries and the total cost of producing those cherries.
Graph Analysis
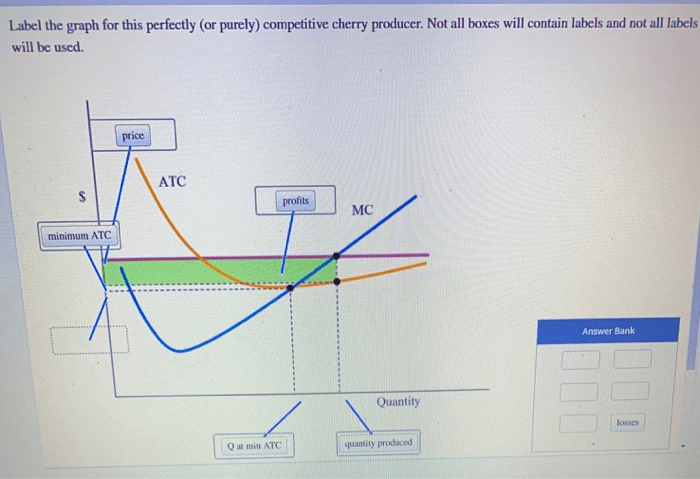
The graph of a perfectly competitive cherry producer shows the relationship between the market price of cherries and the quantity of cherries that the producer is willing and able to produce. The axes of the graph are labeled as follows:
- The x-axis shows the quantity of cherries that the producer is willing and able to produce.
- The y-axis shows the market price of cherries.
The equilibrium price and quantity are the point at which the supply and demand curves intersect. At this point, the producer is producing the quantity of cherries that consumers are willing and able to buy at the price that the producer is willing and able to sell them.
Producer’s Perspective
The cherry producer determines its profit-maximizing output by equating marginal cost to marginal revenue. Marginal cost is the cost of producing one additional unit of output, and marginal revenue is the revenue from selling one additional unit of output. The producer will produce the quantity of cherries at which marginal cost equals marginal revenue.The
producer’s output decision affects the market price of cherries. If the producer increases its output, the market price of cherries will decrease. This is because the increased supply of cherries will lead to a lower equilibrium price.
Market Equilibrium: Label The Graph For This Perfectly Competitive Cherry Producer
The interaction between producers and consumers determines the market equilibrium. The equilibrium price is the price at which the quantity of cherries that producers are willing and able to produce is equal to the quantity of cherries that consumers are willing and able to buy.Supply
and demand play a key role in establishing equilibrium. The supply curve shows the relationship between the market price of cherries and the quantity of cherries that producers are willing and able to produce. The demand curve shows the relationship between the market price of cherries and the quantity of cherries that consumers are willing and able to buy.
The equilibrium price is the price at which the supply and demand curves intersect.
Policy Implications
Perfect competition has several implications for government policy. One implication is that government intervention is generally not necessary to ensure an efficient market outcome. This is because the market will naturally reach equilibrium, and the equilibrium price and quantity will be efficient.However,
there are some cases in which government intervention may be necessary. For example, government intervention may be necessary to prevent monopolies from forming or to correct for externalities.
Answers to Common Questions
What is perfect competition?
Perfect competition is a market structure characterized by numerous buyers and sellers, homogeneous products, perfect information, and freedom of entry and exit.
How does a perfectly competitive cherry producer operate?
A perfectly competitive cherry producer operates by taking the market price as given and adjusting its output to maximize profits.
How is the equilibrium price and quantity determined?
The equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the intersection of the supply and demand curves.